Hey, we get wise. The URL structure is a difficult SEO topic. It’s not easy to master, but not impossible, either. In fact, we’re here to form things easier for you.
In this article, we’ll try to answer all your questions and provide examples for a better understanding of how the structure of your URLs influence your SEO strategies.

Even if you own an eCommerce website or are struggling with Local SEO and WordPress, after learn this article you’ll know how to set up your website’s URL structure for immense SEO answers.
So, keep on reading.
What Are URLs ? Why Are URLs Important for SEO ? Does URL Structure Affect Google Rankings ? URL Structure& User Experience URL Types: Static URLs vs. Dynamic URLs Click Depth vs. URL Structure Subdomains vs. Subfolders Trailing Slash vs. No Trailing Slash Best URL Structure for Local SEO& WordPress The Best URL Structure for eCommerce Websites URL Structure Mistakes Best URL Structure for SEO( Tips& Tricks ) Does Google Plan to Get Rid of URLs in the Future ?
What Are URLs?
A URL( short for Uniform Resource Locator) is the address of a resource on the internet.
You can think of it as a regular address, for a house.
Servers and browsers use URLs to access web pages and resources on the web. You type in an address, you reach a web resource. It’s pretty simple on the surface.
Now, of course, “theres a lot of” technical perspectives to Uniform Resource Locators. However, most of them aren’t an issue for the regular network developer, since they’re managed well by servers and stages these days.
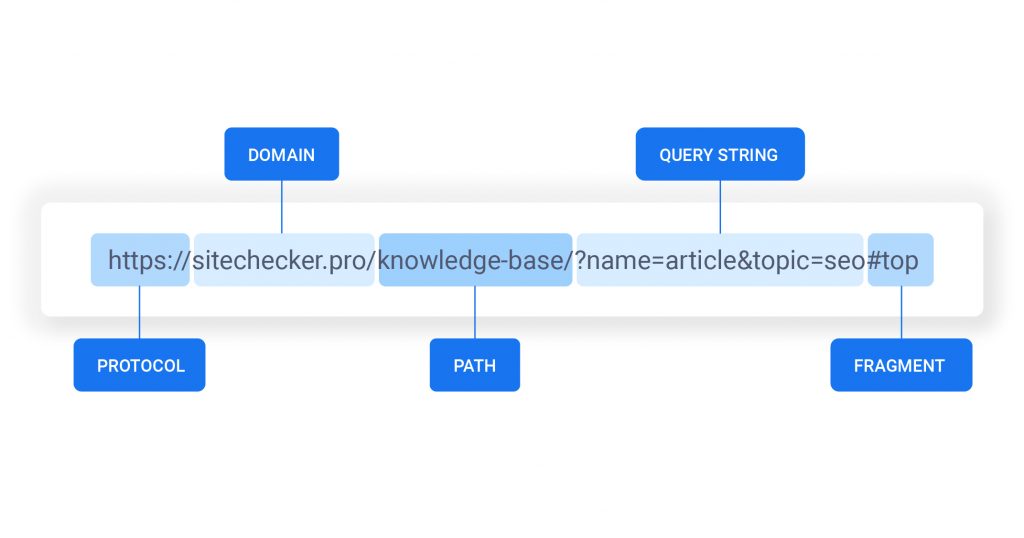
source: https :// sitechecker.pro/
Because stages make it so’ easy ‘, the URL structure of a website is often forgot. It’s not easy to understand and nothing say to you why you should give attention to it.
People end up with large-scale sites and bad URL structures and, unfortunately for them, URL editions are pretty nasty.
Why?
Because they require a lot of patience and double, if not triple check-ups to make sure nothing goes wrong.
If you mess things up, you can end up with a big drop in all your rankings.
So, it’s a lot better if you get things right from the beginning instead of fixing them later, when the site is big.

Why Are URLs Important for SEO?
A lot of search engine optimization experts say that the URLs are very important for SEO.
So, are they?
Well … yes, they are.
A URL is important as it’s a connection between the user and your content.
Google shouldn’t really care what your URL is as long as it’s compliant, indexable& peculiar. But what does this convey accurately?
What’s really important is what’s behind that URL # thecontent.
Many say the URL needs to be short but, in my personal experience, Google administers long URLs just fine. And they can rank well too.
So, only “refining” your URLs perpetually won’t help you very much to achieve true-blue SEO success.
There are other, more important, OnPage SEO tasks to attend to.
What Google actually cares about in relation to your URLs is your site’s structure.
Structure is related to your URLs, but also to click magnitude, which we’ll soon talk about.
The good thing with URL structure is that you just have to set up things right once( for the bigger picture ).
Then, merely follow a simple list of best practices( which I’ll share with you soon) when creating brand-new URLs.
Does URL Structure Affect Google Rankings?
URLs is absolutely influence SEO.
There are a number of issues that are related to URLs that can affect your higher-rankings. Two of the most important ones are keywords and length.
First of all, you have to make sure that your URLs are valid. Merely use the admitted URL characters. If you don’t know what the issue is, then the best thing to do is to stick to letters, figures and hastens. Not stresses, but dashes.
As Google recommends 😛 TAGEND
Consider using punctuation in your URLs. The URL http :// www.example.com/ green-dress.html is much more useful to us than http :// www.example.com/ greendress.html. We recommend that you use hyphens( -) instead of highlights( _) in your URLs.
Keywords in the URL can also help you rank better for a specific phrase. For example, if I want to write for” Site Explorer” it’s a good idea to have my URL as/ site-explorer.
Having something completely irrelevant in the URL can negatively impact the higher-rankings of that sheet, as the URL should be descriptive of the contents within the page.
So that’s why it’s a good idea to do some keyword experiment before writing your URLs. You can be utilized our Keyword Research Tool.
Another important factor is the URL length. This isn’t an official ranking factor, but there is a strong correlation between shorter URL length and higher rankings.
It’s a good idea to read this entire commodity to find out how to have the best URL structure for your website, as it can definitely have an impact on your rankings on the long term.
URL Uniqueness
A URL has to be peculiar. Well … there’s no other way around it, actually. You can’t have two of the same URL and not shore in the same place.
What you need to understand is that there’s a big link between URLs and content.
Google likes planning material to a single URL. That realizes it unique.
Can You Have the Same Content on Different URLs?
Have the same piece of content on different URLs and Google won’t like it.
For example, duplicate content is mainly considered a content problem when, in reality, it’s strongly linked to URLs.
Don’t believe me? Let me demo you what I’m talking about 😛 TAGEND
You have a product that fits two categories on your locate. That’s perfectly fine. However, if your standard website URL structure is an hierarchical one, then the product might establish on two different URLs( with the same content ).
So we could have a plant-A in the category green-plants but also in tall-plants. If the URL structure is hierarchical, it will gape something like this 😛 TAGEND
domain.com/ tall-plants/ domain.com/green-plants/ domain.com/ tall-plants/ plantA domain.com/green-plants/plantA
This way, domain.com/ tall-plants/ plantA and domain.com/ green-plants/ plantA both emcee the same content, which prepares it reproduce content.
That’s why, for big-hearted eCommerce websites, it’s a good idea to separate the products from the categories. This path you could have 😛 TAGEND
domain.com/ categories/ tall-plants domain.com/categories/green-plants domain.com/ plants/ plantA domain.com/plants/plantB
Talking about ecommerce, if you need to extract data from ecommerce websites, check out this article.
This issue above is strongly related to structure. If you structure your website in a hierarchical acces without considering the above mentioned, you’re bound to have repeat content issues.
Of course, sometimes you can use hierarchical organizations to your advantage, such as when you have a simple neighbourhood website with presentations.
domain.com/ business/ digital-marketing/ ads domain.com/services/digital-marketing/seo domain.com/ assistances/ labelling/ emblem domain.com/services/branding/design
If you know that’ logo’ and’ motif’ are bound to the’ branding’ list and’ ads’ and’ seo’ are bound to the’ digital market’ list, then there’s no issue in keeping them like that. It actually induces feel to do so!
URL Structure& User Experience
Many SEOs say that URLs are important for a user’s experience. Let’s see why.
Usually, you end up on a website either through the beginning domain name or from another website, through a link.
You’ll rarely form in https :// cognitiveseo.com/ blog/ list/ case-studies/ in the browser to access that page.
Most probably, you’ll got to go through the Google search results or via our piloting menu.
Even if it was for you to access that URL from another website, it is very likely working under an fix verse, like this: SEO Case Studies.
Google has been making great efforts to shorten/ conceal the presentation of URLs in the browser, if not removing URLs wholly. (Yes, indeed … well talk more about this at the end of the commodity .)
Sure, a very long URL can appear shady and intimidate people from clicking it.
What would you preferably sounds?
https :// cognitiveseo.com/ blog/ list/ case-studies/
or
https :// www.google.ro/ investigation? safe= active& sxsrf= ALeKk0 3mlWIPa2ZmKmvUqRUZXkcfViGLTQ% 3A1583311321632& beginning= hp& ei= 2WlfXsqWJI_ergSCv7BI& q= cognitiveseo& oq= cognitiveseo& gs_l =p sy-ab. 3..35 i39l2j0l8. 336.1502 .. 1638…0.0..1.176.1258.9 j3 …… 0….1.. gws-wiz ……. 0i203j0i10. 0ZJhf6POO0Y& ved= 0ahUKEwiK55GntoDoAhUPr4sKHYIfDAkQ4dUDCAY& uact= 5
Well, if it comes from a reliable source( such as a friend ), you’ll probably click it. But otherwise, most probably, you won’t.
From what I know, the longest URLs on the web are Google search results sheets and links with Facebook ID parameters. Please feel free to share your opinion on this matter on the comments segment below.
URLs are, nonetheless, important for a blogger’s experience.
If you want to get backlinks, you want to become your URLs appealing.
You don’t want to discourage a blogger to share your post on social media or link to your site from their blog posts.
That’s what I think an’ SEO Friendly URL’ signifies. So keep your URLs pretty.
URL Types: Static URLs vs. Dynamic URLs
URLs can be split into two categories. You have dynamic URLs and static URLs.
But which ones should you use?
Websites, especially eCommerce storages, have both static and dynamic URLs.
In fact, any programme which has a database probably has some sort of dynamic URL protocol.
So if I set up a basic HTML website, those would be true static URLs. When I have a platform with a database and I’m trying to pull information from that database( let’s say eCommerce filters, such as complexions and sizings) the platform are creating dynamic URLs.

In Google’s attentions, all URLs are’ static’. Once they’re indexed, it’s done. Change it without a 301 and Google will consider it gone and derank it.
The issue with dynamic URLs is that there’s an infinite sum of URLs that can be generated. That happens because of filters.
If you’re not careful, you won’t be able to keep track of them easily.
It’s a good idea to avoid too many parameters in a single URL. Limit them to 2 or 3.
This usually occurs when people add too many irrelevant filters and index too many pages.
Most of the time, people index all the parameters, which is a bad practice. Why index a sheet if it doesn’t have any explorations?
Make sure that the parameters you’re letting Google index actually have searches. So if you have a sweater in 10 emblazons, see if parties search for all those colors.
If not, indicator simply the ones that do have searches.
Thus, if people simply sought for’ red sweaters ‘, then you will simply indicator domain.com/ supermarket/ sweaters? dye= red. This be interpreted to mean that? color= off-color,? shade= black would remain unindexed.
Moreover, keep your parameters in an ultimate seek!
What does that mean? It means that if your customer selects the dye firstly and then the length, the URL will be? pigment= red& sizing= small but if he adopts the sizing firstly and then the complexion, the URL will still be color= red& size= small.
So the order of the parameters in the URL doesn’t change. It’s the better option.
Sometimes, it’s not easy to set up a suitable faceted navigation that benefits both the user experience and SEO.
If you want to set up a filtering menu properly, read this article about Faceted Navigation& Filters.
Canonicalization
Keeping an ultimate degree is not ever easy to achieve. You’ll need a good entanglement developer.
In case you can’t obstruct absolute lineup for parameters, canonicalization is an easy alternative.
So if “youve had” both URLs (? emblazon= red& length= small-time and? length= big& pigment= red) you can simply pick one as the main URL.
Remember to likewise self canonicalize the central URL.
Therefore, if? hue= red& immensity= small is our main URL, it would have a rel =” canonical” to? pigment= red& size= small-scale and then? size= big& coloring= red would have a rel =” canonical” to? complexion= red& size= small.
Confusing, I know, but very important. You can find out more about canonical labels& URLs now.
301 Redirects
I want to make sure I too cover 301 redirects in this article, because they’re really important.
If you simply move a web page from one URL to another, Google will really reviewed and considered the old page run and the brand-new page a fresh one.

Source gomage.com
This means that it has to rank it again, which means you’ll lose the positions of the old one and have to put up all the work again to rank the brand-new one.
To keep the higher-rankings and shape Google understand that the old page simply changed its spot, you have to use 301 redirects.
You probably know all that, but you’d be surprised how many people forget to properly 301 when melding websites. This has cataclysmic importances, so make sure you properly 301.
It’s also a good mind to avoid redirect series. So, it’s better to have A> C and B> C than A> B> C.
If you’re looking for SEO implements that can trace redirect chains, the CognitiveSEO Site Audit is a good choice. You’ll locate what is necessary under Architecture> URLs/ URL Chains.
Click Depth vs. URL Structure
URLs are about technical SEO. Not so much user oriented. Click depth, on the other side, is very user oriented.
Remember when I said that click depth too matters in the site’s structure?
Your site’s structure reflects itself in the sound breadth and your useds react to it.
The more users have to click to get to where they miss, the least likely “theyre trying to” convert.

The same thing goes with Google. The deeper the click penetration to a sheet, the less significant Google thinks it is.
Click Depth is also technological, but it indicates the human behavior, more specifically users’ interaction with your website.
Click depth concerns for SEO. We could even say it’s one of Google’s grading signals. In fact, Google official John Mueller said it himself.
Now if “youre reading” my stuff in general, you know I’m not a big fan of must go after what John Mueller says.
However, in this case, there’s a lot of proof to back it up.
Breadcrumbs
Breadcrumbs can be a sketch of your site’s structure.
There are multiple directions you can implement breadcrumbs on your site.
The first would be in relation with the URL and place organize and the second largest in matters relating to the user’s clink path.
It’s better to implement the first one, in general. A user’s clink move can also be followed via the back and forward buttons in the browser.
You likewise have more restraint on offsetting the breadcrumbs useful to the user if you organize your locate properly.

For example, if you register the featured commodity Tuna on the Homepage and the subscribers sounds it, a history based breadcrumb organisation would generate Home> Tuna.
Not very useful if the subscribers too want to wish a different type of fish.
Instead, if I have the domain.com/ categories/ fish/ tuna I can have Home> Categories> Fish> Tuna, irrespective of where the subscribers comes from on that page.
The breadcrumbs can( and should) be hierarchical, even though they are the URL structure isn’t.
This means that I can have domain.com/ shoes/ feeing/ and domain.com/ products/ nike-xyz
Home> Shoes> Running> NikeXYZ where’ NikeXYZ’ would link to domain.com/ concoctions/ nike-xyz,’ Running’ would link to domain.com/ shoes/ passing and’ shoes’ to domain.com/ shoes, while the Home breadcrumbs will link to domain.com.
You can see how the site’s structure doesn’t ever indicate in the URL path.
Subdomains vs. Subfolders
When structuring your site, there’s always the option of using subdomains.
A subdomain is what’s before your seed domain name. Thus, tools.cognitiveseo.com is a subdomain, while cognitiveseo.com/ blog is a subfolder.
Subdomains act … kind of like separate websites.
Many say there’s no difference between using subdomains vs. utilizing subfolders, but many have also accompanied proof that it’s safer to use subfolders.
If your internal links programme must be drawn up properly, subdomains was necessary to succeed very well.
While subdomains can rank properly, if you don’t know what you’re doing it’s better to stick with subdirectories.
Trailing Slash vs. No Trailing Slash
I’m just going to keep this brief: it doesn’t matter.
Just make sure you keep it consistent and properly 301 to the main version.
Google treats https :// cognitiveseo.com/ blog/ 23628/ url-structure/ and https :// cognitiveseo.com/ blog/ 23628/ url-structure as separate URLs.
If you don’t use 301, both sheets will get indexed and they will cannibalize each other.
In the old days of the internet, most web pages would have an extension as they were all seen as file epithets( such as page.html ).
The trailing slash would represent a folder instead of a folder, but today that’s not the case anymore. Merely be consistent and 301 properly.
Relative URLs vs. Absolute URLs
Links can be absolute URLs or relative URLs.
Absolute URLs include the protocol, subdomain, subfolder and everything else after.
An absolute URL would be https :// www.website.com/ sheet/ subpage /.
A relative URL “wouldve been”/ sheet/ subpage /.
It’s very important to use relative URLs merely on your website and ultimate URLs on other websites.
So, if you do connect improving to get backlinks, make sure you always utilize absolute URLs.
For Google, it doesn’t really stuff which one “youre using” on your website, but it can affect you if you want to change your domain name or switch from HTTP to HTTPS.
If you use absolute URLs as part of your internal associate approach, when you convert your land, those ultimate URLs would be maintained, thus still connecting to the old-fashioned domain.
Sure, you will have 301 redirects set up, but it’s always better to have the brand-new orbit in all your internal links.
So make sure that when you do internal linking, you use relative URLs if possible, so when you make any changes to your realm, the scaffold can take care of everything and you won’t “re going to have to” manually supersede thousands of links.
Best URL Structure for Small Site, Local SEO& WordPress
Small websites can have hierarchical URL structures, as previously mentioned. Just make sure you won’t cause duplicate material issues.
If you’re targeting multiple locations, then you should have separate sheets for each locale you’re targeting.
I know, numerous might say that these are doorway sheets and that Google penalise them.
However, they’ve been proven to work countless experiences. There’s also no alternative to doorway pages.
Keep it relevant and Google will reinforce you.
If you have a WordPress blog, then you most probably want to keep the pages immediately following the root URL.
We’ve separated our blog under/ blog because we have a separate WordPress install in/ blog which procreates it is not possible to for us to place essay URLs immediately after the spring domain name.
You might also notice the numbers after the blog. That’s an identifier, which was a technological necessity some time ago. It’s better if you don’t have those.
So, if you can, go for https :// cognitiveseo.com/ url-structure/ instead of https :// cognitiveseo.com/ blog/ 23628/ url-structure-seo /.
If you’re wondering why we’re not doing this, here’s the answer: We could remove them, but it would require a big effort mapping all the articles for 301 redirects and we don’t consider this would have a big/ positive impact on your rankings.
Our website has several functionalities and is pretty big and complex. We have our tools arriving pages in our seed domain, it is therefore establishes ability to separate our blog in the/ blog subdirectory.
If you just have a blog, then keep URLs immediately following the beginning. Brian Dean’s blog on Backlinko.com is a good example.
Avoid using the time in the URL if your pole is evergreen. This will prevent consumers to sounds your result in the future and will likewise compile Google think your content is’ old’.
The Best URL Structure for eCommerce Website
When it comes to eCommerce websites, things aren’t that simple with URLs.
The safest way to go for it is to separate each section in its own subdirectory.
This means that you’ll need a/ blog/ or/ articles/ prefix for your commodities and uprights, a/ produces/ prefix for your makes and a/ lists/ for your lists and so on.
This helps you keep track of your pages. If you every crawl your website to analyze it … it will be a nightmare to analyze the information if all the post types were in the spring domain.
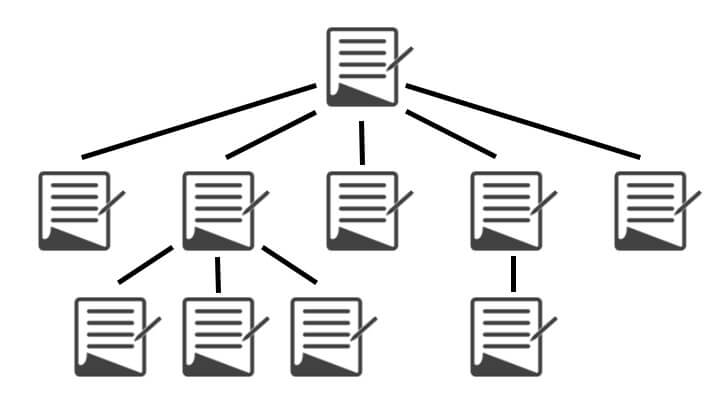
Source: searchengineland.com
Make sure you don’t add too many subcategories. Remember, try to keep the click depth … shallow.
Take advantage of the breadcrumbs recommendations I’ve made above.
Make sure you know exactly which URL constants/ filters you indicator and which you don’t.
You should definitely read this article about Faceted Navigation for SEO
URL Structure Mistakes
There are some things that you must definitely forestall when drawing up your URL structure.
Here’s a list of the top biggest mistakes that webmasters draw when they form their URLs.
Changing URLs without 301
As you’re on a sheet about URLs, if your design is bad or you’re contemplate on varying it, then I can’t stress this enough.
Your positions will remove if you don’t properly 301 from the age-old sheets to the new ones.
Remember, if you convert the URL, you MUST use 301 redirect from the old one to the brand-new one.
Having several variants
One problem that countless websites have is not properly redirecting all the discrepancies of the site to a single one.
For example you are eligible to have HTTP and HTTPS and then with WWW or without WWW.
This develops in 4 versions which Google sees as separate places, in a manner that is 😛 TAGEND
http :// cognitiveseo.com https://cognitiveseo.com http :// www.cognitiveseo.com https://www.cognitiveseo.com
Make sure you pick one and 301 redirect all the others to it.
You can predict more about which explanation you should choose in our article about WWW vs non-WWW.
Having several URLs for the same content
Sometimes, it can happen the different URLs have the same content. This is called duplicate content and it can happen often in eCommerce websites.
You can have, for example, two filter constants such as’ red’ and’ small’.
However, if everything your red concoctions are small and all your small products are red, those sheets will predominantly be identical.
This is just a hypothetical precedent, but things can scale pretty quickly, starting hundreds if not thousands of highly very similar URLs with not much value.
If you want to read more about how to work around this issue, check out our Faceted Navigation Guide.
Using’ bad’ references
Browsers exclusively subscribe certain people in the URL.
Most content management systems know how to handle these and will divest them from the URL if you add them unknowingly.
It’s best to avoid parameters and involved URLs, at least for the sheets you want to be indexed and ranked well.
Google can direct parameters with multitudes and other attributes, but most of the pages you want to rank high for highly competitive keywords is advisable to static URLs with keywords in them.
Using too many subdirectories& lists
If you have an eCommerce website, try to keep things short-lived. Don’t include many hundreds of layered subcategories. Only computed the important ones.
A good doctrine to know which ones are important is to do proper keyword research. If none searches for those calls, maybe don’t contribute them as subcategories.
You might have some granular formation that seems important, but if users simply sought for the 5th elevation, then maybe make it the first or the second and trimmed the other ones.
Keeping everything in root region
When you initiate the structure of the site, make sure to separate different articles
Some web originals consider that the shorter the URL, the very best. But not in every speciman!
If you have a blog on a certain topic, such as Backlinko.com, it might make sense to keep everything in the spring subject. You have very few pages and it’s easy to manage.
However, if you have a big site, and you have works, products, commodities, points and so on, it will be a nightmare to analyse the website after a slither if everything is in the spring domain.
Not applying keywords or using too many keywords
Make sure you have some of the largest part keywords the subscribers are searching for in your URL.
Not having keywords at all is a very bad idea, especially if you have only crowds, or times or so.
So if you have an article about really good rock parties don’t let your URL be site.com/ 03/03/ 2020/ article-1 523 but instead have it site.com/ top-5-rock-bands- 2020.
On the other side, it’s a good idea to not have the keywords too many times. It gazes spammy and Google can pick up on that.
Avoid creating duplicate iterations of the keywords in the URLs.
This can happen often on eCommerce websites, when creating categories and not editing their URLs.
The content management system will merely pick up the name of the sheet, and the hierarchical URL structure will look like this.
musicsite.com/ containers/ acoustic-drums/ acoustic-drum-accessories/
A better alternative would be 😛 TAGEND
brandsite.com/ containers/ acoustic/ accessories.
Best URL Structure for SEO( Tips& Tricks)
There is no clear best URL structure for SEO as this depends on very many causes. However, in order to maximize the search engine optimization benefits, make sure to follow these best practices for SEO friendly URLs.
Use Keywords in Your URLs:
Keywords is important for SEO. It’s a good idea to add them in your URL. These URLs are announced semantic URLs.
It’s more important to have your target keywords in your claim tags and material than in the URL.
However, lending them in the URL can bring some benefits 😛 TAGEND
For formerly, if customers examine really at the URL, they’ll know what it’s about.
Secondly…
If you do attach improving to your page without exploiting keyword rich secure texts, the URL will act as the secure text so it’s a good idea to have the keywords there!
You can streamline URLs by removing short or less explanatory utterances such as stop texts. Here are some stop names illustrations: to, the, how, and, for, it, a, why.
For example, instead of/ how-to-jump-really-high/ you could just go for/ jump-higher/ or/ improve-jumping /.
You don’t always have to remove the stop names from your URL.
For example, you might have the target keyword” how to cook” where the URL domain.com/ how-to-cook/ is just perfect.
It’s also a good project to add the main keyword in the URL, if you have one and it also has searches.
In this case, it fits my essay: parties sought for” url design seo” and my URL is/ url-structure-seo /.
But people too sought for” how does URL structure feign SEO “. Why didn’t I select this keyword phrase as my URL?
Because the first one has more examinations I’ll let you figure out the rest.
If you’re looking for SEO tools that can check that for you on a large scale, make sure to check out CognitiveSEOs Site Explorer. You’ll catch what you’re looking for in the Architecture> URLs section.

CognitiveSEO Site Audit URL Analyzer Tool
Keep the URLs Short:
The popular opinion is that shorter URLs rank better.
While I personally still have to investigate this matter, I still keep my URLs short and to the point.
Why? Because they are better for user know. Here’s how our most important pages URLs are 😛 TAGEND
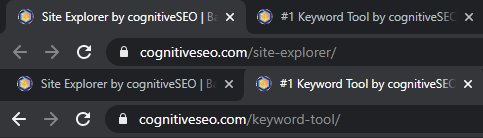
On a WordPress platform( not our subject for the primary area ), they would be generated using data from the post title.
Content management systems such as WordPress would strip some elements that are incompatible, so they would be like this 😛 TAGEND
cognitiveseo.com/ site-explorer-by-cognitiveseo-backlink-checker-link-research
cognitiveseo.com/ 1-keywordtool-by-cognitiveseo-keyword-explorer-content-optimization
Not … horribly, but not very good either.
And it’s also on the safer back to keep them short. If URL length does actually matter for OnPage SEO, better have it suddenly rather than long, right?
While there’s a correlation between shorter URLs and high higher-rankings, it doesn’t 100% aim it’s because of the shorter URLs.
Maybe very well optimized places likewise like to have prettier, shorter URLs.
However, don’t try to attain them too short. For example, some implementation/ p/ instead of/ commodities/ and/ c/ instead of/ categories /.
I don’t think that’s necessary. In fact, I consider it examinations more spammy.
Too short-lived might also planned removing some important keywords
Keep URLs Unique
Make sure you don’t once have very similar sheets before you write and publish a new page.
If you do, it might be a good idea to better optimize the other page instead, or target a different topic/ established of keywords for the new one.
Use Hyphens Instead of Underscores& Avoid Special Characters in Your URLs
Hyphens and underscores seem very similar, but on the internet they’re treated jolly differently.
Google recommends that you should bypassed stress in your URLs. They can cause issues.
Underscores are treated as word joiners by Google, while rushes as text separators.
People are also used to smashes more. So your URL should be url-structure-seo not url_structure_seo.
Also, avoid any special characters in your URL, except the basic ones used for parameters and linchpins such as?&= #.
Most platforms won’t even let you make love but, if your URL contains reputations such as, or; or ‘, it can cause problems.
If you don’t know what a special character necessitates or does in a URL, then it’s better not to use it.
Of course, there’s also the trailing lash /, which is ok to use.
Use as Few URL Parameters as Possible
Parameters can add to length and they too make a URL glance
However, in certain situations, they also lend keywords in your URL which can be a good thing if parties search for those keywords.
Remember to only index the pages people actually search for instead of every possible filter combination your area can come up with.
Prioritize& Think about Click Depth
Don’t add too many deep pages, such as subcategories inside subcategories #inception.
Keep it short and to the point.
If you do have a lot of deep pages who play an important role, make sure you use internal ties in your blog berths or other articles of your website so that Google can properly find them.
You can also share these pages on social media or other websites from time to time.
Avoid Hierarchical URLs When You Have a Site that Changes Often
This runs chiefly for eCommerce or any site that is very dynamic, such as news locates, car trading places, incidents places, etc.
You can use hierarchy if you’re sure a resource won’t change its parent.
Don’t Stuff Keywords in Your URLs
Keyword stuffing is bad in content, bad in name tags and bad in URLs.
Don’t get it on!
Sometimes, people stuff in keywords in their URLs by mistake.
Example: randomshoeswebsite.com/ shoes/ running-shoes/ running-shoes-for-women/ red-running-shoes-for-women/ nike-running-shoes-for-women/
I’m not sure it’s the best illustration, but I hope you get the point.
Instead, maybe go for something like: randomshoeswebsite.com/ shoes/ guiding/ wives/ nike/ red /.
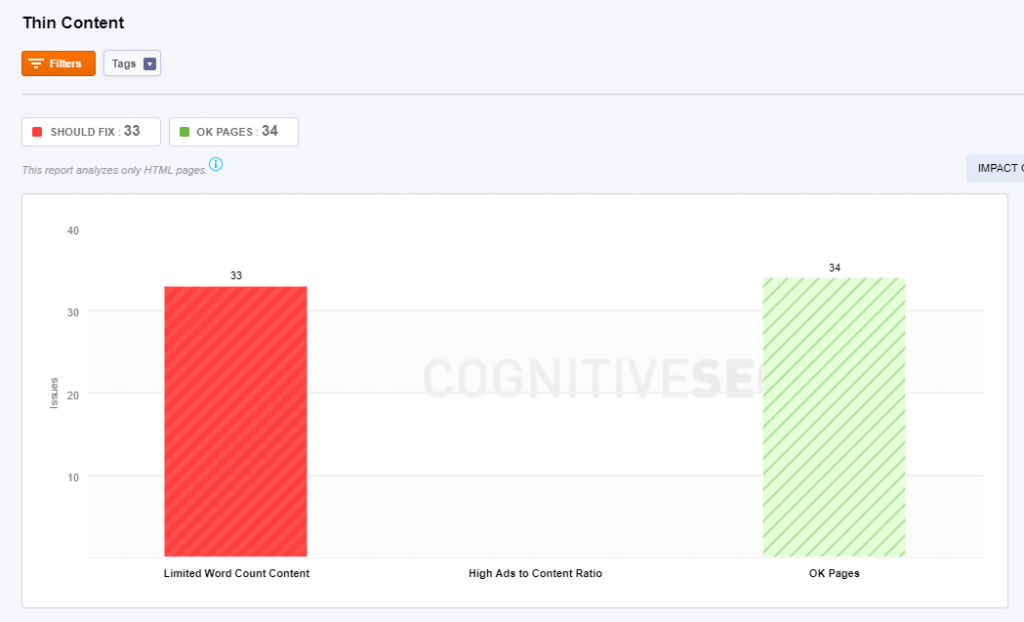
Avoid Duplicate, Similar& Thin Content
Again, duplicate questions are chiefly is generated by good URL structure implementation, bad canonicalization and indexation practices.
Make sure you don’t have very similar sheets on your website or they will impact your overall website SEO performance.
If you’re looking for SEO Tools that they are able choose reproduce content problems, then the CognitiveSEO Site Audit Tools is perfect for you. You got to find what you’re looking for under the Content Section.
Does Google Plan to Get Rid of URLs in the Future?
It might be the case that, in the future, Google will haunt its dream of getting rid of URLs.
The first step would be not to display them at all, first in the search results and then in the browser itself.
However, get rid of URLs
This all started with Google AMP, where Google caches the financial resources on their network servers, therefore exposing them on their terrible URLs, which they then hid.
If you want to know more about the subject, spoke this article about Google trying to remove URLs.
Conclusion
The URL structure of your website is important. Don’t negligence it! You merely have to set it up right once.
Once you organize things properly, merely follow the very best traditions. Add your target keywords, “ve been thinking about” URL length, avoid keyword stuffing, restriction irrelevant URL constants and you’re good to go.
How did you set up your URL structure? Let me know in the comments section below!
The post URL Structure. Dos, Don’ts and Best Tradition for SEO performed first on SEO Blog | cognitiveSEO Blog on SEO Tactics& Strategies.
Read more: cognitiveseo.com






Recent Comments