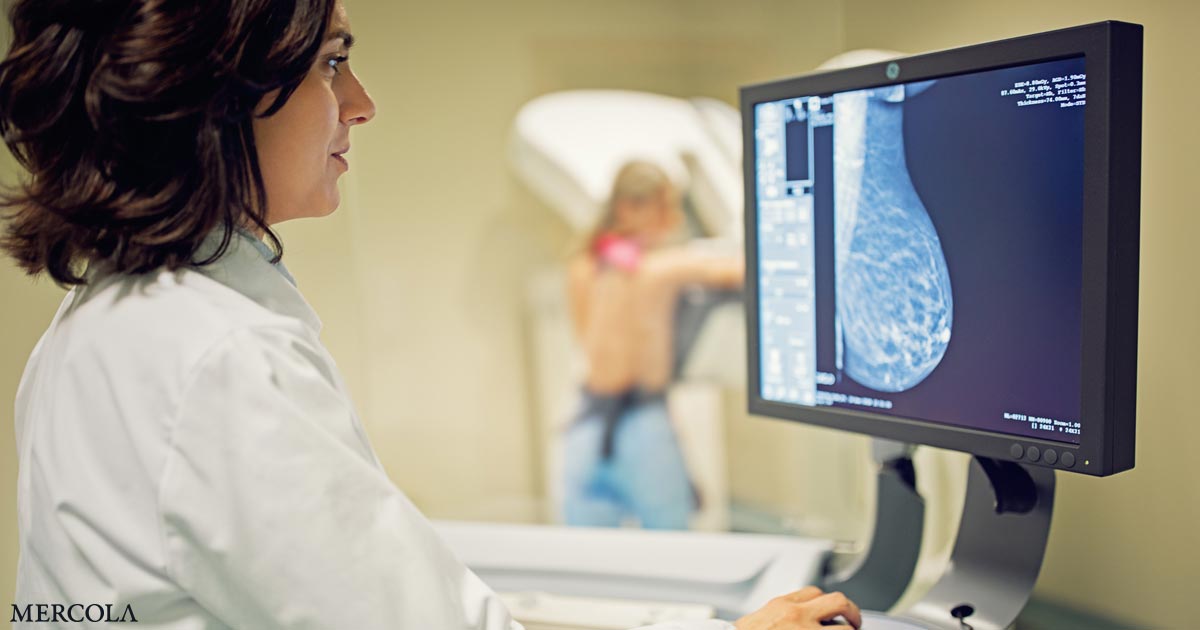
When asked how much radiation maids are to be subject to from mammograms, Dr. Ben Johnson, generator of “No Ma’am-ograms, ” says, “At least the quantities of 100 dresser X-rays.”
It’s a statement that would stun many women who are advised to receive a mammogram as the standard of care for breast cancer prevention in the U.S. — and it’s simply one of the eye-opening information presented in the documentary “Boobs: The War on Women’s Breasts.”
The film begins with a written statement informing observers that everyone is of the information you’re about to hear encouraged by scientific literature, even if they are much of it opposes the pronouncements make use of conventional drug. Physicians from around the United Country and various regions of the world — including California, Georgia, Switzerland, Virginia and Arizona — are interviewed, adding expert testimony on why you may want to rethink this contentious procedure.
The’ Early Detection’ Myth and Biopsy Risks
One myth continued by conventional medication is that mammography is the most important screening exam for breast cancer because it can detect breast cancer “up to two times before the tumor can be felt by you or your doctor.”1
However, the film points out that by the time you can feel a cancerous glob in your tit, the cancer has already been growing for two to 5 year. “Mammograms are not early perception, ” Johnson says.
The myth that mammograms don’t spread cancer is also addressed, via the story of one wife who was diagnosed with theatre 4 cancer and given simply one year to live. She made significant changes to her lifestyle and many of the tumors disappeared. The cancer was stable year later, until she received a biopsy and precede mammograms, which she says attained the cancer spread — and a tumor is indicated in the place where the biopsy was done.
During a biopsy, a piece of tissue from a tumor or organ is removed so that it can be examined under a microscope, often is required to determine whether it is cancerous. Needle biopsies, for instance, are widely used as part of the traditional allopathic approach to diagnosing breast cancer. But they are able to inadvertently start malevolent cells to break away from a tumor, ensuing in its spreading to other areas of your body.
One of the harms of using mammography as a screening implement is that it can often lead to overdiagnosis and overtreatment, including false-positive tests and unnecessary biopsies. 2
One study from the John Wayne Cancer Institute revealed that a needle biopsy is rising the spread of cancer compared to patients who receive excisional biopsies, also known as lumpectomies. 3 They concluded, “Manipulation of an unscathed tumor by FNA[ fine-needle desire] or large-gauge needle core biopsy is are connected with an increase in the incidence of SN[ sentinel node] metastases, perhaps due in part to the mechanical disruption of the tumor by the needle.”4
Johnson said he calls biopsies “the kiss of death, ” describing how the needle gets driven through a billion cells, blows through the cancer and travels out the other side, dragging cells back through and spreading the cancer. Dr. Manfred Doepp, medical director of the Couros Center in Switzerland, agrees that biopsies can spread cancer, while the physical behave of constricting the tit during mammography may also trigger the cancer to spread.
The film quotes a rapid response published in the BMJ, which nations “robust technical data, published in prestigious medical magazines, have lent meaningful support to the concept” that the squeezing flow of mammography is in itself potentially harmful. 5
Breast Cancer Overdiagnosed in 1.3 Million Dames
The notion that mammography is an accurate screening implement is another myth busted in the film. Both false positives and untrue negatives occur, and even the ability of the radiologist in learn the mammogram is a factor in whether or not mammography can be used to detect cancer.
Overall, when researchers examined trends in early-stage breast cancer and late-stage tit cancer from 1976 to 2008 to the women 40 years and older, they discovered the introduction of mammography in the U.S. is connected with a doubling in the numeral of early-stage breast cancer specimen spied every year. 6
However, the pace at which maids developed late-stage cancer decreased by 8% during that era, conducting the researchers to suggest that only a small number of early-stage cancer diagnosed would progress into advanced disease: 7
“Despite substantial increases in the number of cases of early-stage breast cancer detected, screening mammography has only marginally shortened the rate at which wives present with advanced cancer.
Although “its not” certain which women have been affected, the inequality therefore seems that there is substantial overdiagnosis, accounting for almost a third of all freshly diagnosed breast cancers, and that screening is having, at best, exclusively a small accomplish on the rate of death from breast cancer.”
They concluded that due to the introduction of mammography, breast cancer was overdiagnosed — meaning that tumors were detected that would never to be translated into clinical evidences — in 1.3 million gals over a 30 -year period.
Up to 80% of Breast Biopsies Are Benign
The overdiagnosis of breast cancer comes with serious jeopardies, including needless treatments and wasteful stress and feeling. In another study was indicated in the cinema, it’s stated that more than 1 million heart biopsies are accomplished yearly in the U.S ., 75% to 80% of which turn out to be benign. 8 Sometimes, the benign answer isn’t unveiled until an wasteful mastectomy has already occurred.
Up to 1 in 4 breast tissue biopsies may be incorrectly diagnosed by pathologists, 9 and wasteful mastectomies have been accomplished as a result. In a dispute that went to trial in 2020 in Israel, a woman was diagnosed with breast cancer after a biopsy researched at two medical cores “re coming back” positive.
She underwent six months of chemotherapy as a result, as well as a partial mastectomy to remove the growth. After the swelling was removed, the lawsuit alleges, it turned out to be benign. 10 In 2015, researchers with Boston Children’s Hospital in Massachusetts revealed that false-positive mammograms and breast cancer overdiagnoses among women ages 40 to 59 rate the U.S.$ 4 billion each year. 11
Mammograms May Not Work for Women With Dense Breasts
The story of Nancy Cappello is also covered in the film. Cappello was diagnosed with breast cancer after receiving two ordinary mammograms. The cancer was missed because she has thick-witted tit tissue, and was only disclosed when her doctor felt a crest in her breast and prescribed an ultrasound test in addition to a mammogram.
Cappello was a explorer in the free movement of persons to school girls about thick-witted heart tissue and how exercising a mammogram to detect cancer in such material is “like finding a polar allow in a snowstorm.” She said: 12
“So I gone on a search — for investigate — and I detected for nearly a decade BEFORE my diagnosis, six major studies with over 42,000 females concluded that by supplementing a mammogram with an ultrasound grows perception from 48% to 97% for women with dense tissue.
I likewise learned that women with terribly thick-witted tissue are 5x more likely to have breast cancer when compared with women with fatty breasts and that experiment on dense heart material as an independent hazard part for breast cancer has been studied since the mid 70 s.
… I tolerated a mastectomy, renovation, 8 chemotherapy managements and 24 radioactivity medications. The pathology report fortified — theatre 3c cancer because the cancer had traveled outside of the tit to my lymph nodes. Eighteen lymph nodes were removed and thirteen contained cancer — AND REMEMBER — a “normal” mammogram merely weeks before. Is that early observation? ”
As a result of Cappello’s movement, 38 countries have passed mandatory heart concentration reporting rules. The movie states that up to 90% of females may have some degree of dense breast tissue that may affect a mammogram’s outcome and could benefit from totality tit ultrasound — a procedure that’s not widely available. Women are also interviewed that were told they had dense tit material, but not what that required for the effectiveness of mammography.
‘Precancer’: Ductal Carcinoma in Situ
Ductal carcinoma in situ( DCIS) refers to the abnormal emergence of cadres within the milk pipes of the breast organize a lesion often between 1 to 1.5 centimeters( cm) in diameter. While the cadres perform malignant under a microscope, they have not infested encircling tissue and are considered “precancer, ” noninvasive or “stage zero breast cancer.” Some experts have also argued that DCIS should be considered noncancerous.
Despite this, the cinema tells the story of one maid who had both hearts removed due to a DCIS diagnosis. Such identifications now represent 20% to 25% of all “breast cancers, ”1 3 and the standard of care is to treat all DCIS with mastectomy or breast-conserving surgery with radiotherapy. Harmonizing to a review in the British Journal of Cancer: 14
“In effect, women with DCIS are named as’ cancer patients’, with concomitant anxiety and negative impact on their lives, despite the fact that most DCIS lesions is more likely to never progress to invasive breast cancer.
Owing to the uncertainty seeing which lesions run the risk of progression to invasive cancer, current gamble feelings are misinforming and therefore bias the dialogue among clinicians and women diagnosed with DCIS, resulting in overtreatment for some, and potentially countless, women.”
Is Radiation From Mammograms Dangerous?
There’s also the issue that mammograms use ionizing radiation at a relatively high dose, which in and of itself can contribute to the development of breast cancer. In a 2016 study, it’s stated, “ionizing radiation as used in low-dose X-ray mammography may be associated with a danger of radiation-induced carcinogenesis.”1 5
They point out that people who carry certain genetic alterations or have an inherited disposition of breast cancer, in particular, should evade ionizing radiation as far as is possible — the latter group being one that conventional medicine often recommends for programme or even additional mammography screening. Again, they direct individuals to a different, safer, word of testing: ultrasound or magnetic resonance likeness( MRI ). 16
A “new and improved” type of mammogram called 3D tomosynthesis, which is basically a CT scan for your hearts, is particularly problematic, as your radiation exposure is even greater than from standard mammograms — and by a significant margin.
According to one study, 17 annual screening use digital or screen-film mammography on maids aged 40 to 80 times is associated with an generated cancer prevalence and lethal breast cancer charge of 20 to 25 specimen per 100,000 mammograms. Meaning, annual mammograms make 20 to 25 an instance of lethal cancer for every 100,000 females going the test.
The 3D mammogram expects several ideas in order to achieve three-dimensionality, so it stands to reason your total radiation exposure would be considerably higher than from service standards 2D mammogram.
Thermography and Ultrasound Use No Radiation
In order to realise informed decisions, girls should be provide such all of their screening alternatives, together with an explanation of their strengths and weaknesses, and be allowed to utilize the option of their alternative.
Mammography is only one alternative, with appreciable handicaps. Other potentially safer options include self and clinical heart quizs, thermography, ultrasound and MRI. Thermography and ultrasound expend no radioactivity, and may spot abnormalities that mammograms miss, especially in women with dense heart tissue.
These are explained in detail toward the end of the movie, but they can be difficult to access in the U.S ., as the billion-dollar mammography industry frustrates the widespread exert of these beneficial tests.
It’s also important understood that mammography doesn’t impede breast cancer in any way. Breast cancer prevention involves a healthful life-style, escape of toxins and attention to specific nutritional influences, such as vitamin D. It is absolutely vital to know and optimize your vitamin D level as it can radically reduce your risk of breast cancer.
Ignoring these factors and simply getting an annual mammogram and believing you’re protected will come to an end solution being foisted upon countless ladies trusting the advice of conventional prescription. By contributing a healthful life, and seeking to get informed about all of your breast cancer screening options, you can avoid this potentially deadly pitfall.
About the Director

I believe in bringing quality to my books, which is why I are intended to share some information about the filmmaker, Megan S. Smith, M.S ., and what went in to compiling “bOObs: The War on Women’s Breasts.” Thank you, Megan, for sharing with us.
What was your muse for making this film?
My inspiration for making this movie, as well as in becoming my next movie on alternative cancer rehabilitations, was the death of my husband 11 decades ago from lung cancer. Specifically, for “bOObs, ” my brainchild was emboldened by the death of my three dear friends in as numerous times after their breast cancer returned following 10 -plus years in remission.
What was your favorite part of making the film?
My favorite part of making this movie was interviewing the patients and doctors. I learned during my interviews of Drs. Ben Johnson and Galina Migalko about the handicaps of mammograms and that we might instead be using thermography in conjunction with ultrasound. This nonradiation etiquette shaped sense to me.
Also, my interview with The American Cancer Society’s Dr. Otis Brawley was an eye opener, as he disclosed, “Mammography is a suboptimal test” and “We need a better test.” All these physicians were discerned on. More information on the movie can be found here.

Read more: articles.mercola.com





Recent Comments