As a Windows user, the Control Panel and the Settings app can feel quite restriction in what they can do. If you demand full and ultimate restrain over your structure, intending access to everything the operating system has to offer, then you’ll have to start using Command Prompt.
Unlock the free “1 00+ Essential Windows CMD Commands” cheat sheet now!
This will indicate you up to our newsletter
Enter your EmailUnlockRead our privacy policy
Never exploited Command Prompt before? Don’t worry. Using it is as simple as typing out the biddings you’ll see below.
If you’re ready to continue, here are some of the most useful networking bids to know for managing and troubleshooting your dwelling network.
1. PING
ping is one of the most basic more helpful system dictations to utilize in the command prompt application. It tells you whether your computer can reach some end IP address or domain name, and if it can, how long it takes data to travel there and back again.
Sample usage and output 😛 TAGEND

The command undertakings by sending out multiple data packets and learning how many of them return. If some of them don’t return, it’ll tell you( “lost” ). Packet loss leads to good execution in games and streaming, and this is a nifty way to test.
By default, it routes 4 containers, each one waiting 4 seconds before timing out. You can increase the number of containers like this 😛 TAGEND ping www.google.com -n 10
And you can increase the timeout duration like this( appreciate is in milliseconds ):
ping www.google.com -w 6000 2. TRACERT
tracert stands for Trace Route. Like ping, it is sending out a data container as a road to troubleshoot any network issues you might have, but it instead moves the roadway of the container as it hops from server to server.
Sample usage 😛 TAGEND

The command outputs a line-by-line summary of each hop-skip, including the latency between you and that special move and the IP address of that move( plus domain name if available ).
Why do you verify three latency reads per-hop?
The tracert network command is sending out three containers per hop to cover packet loss or slowdowns. Precisely remember that it doesn’t represent your true-blue latency. It’s best practice to average the three.
3. PATHPING
pathping is similar to tracert except more instructive, which entails it takes a lot longer to execute. After sending out containers from you to a presented destination, it analyzes the roadway made and estimates packet loss on a per-hop basis.
Sample usage and output 😛 TAGEND

4. IPCONFIG
ipconfig often comes up as the most-used networking command on Windows. Not only is it useful for the information it supports, but you can combine it with got a couple of buttons to execute certain tasks.
Sample usage and output 😛 TAGEND

The default output evidences every structure adapter on your method and how they resolve. The IPv4 Address and Default Gateway details under the Wireless LAN Adapter and Ethernet Adapter segments are the most important to know.
Use this switch to flush your DNS cache 😛 TAGEND ipconfig/ flushdns
Flushing the DNS cache can help when your internet is working, but a specific website or server is unreachable for some reason( e.g. an internet site hours out and won’t load ). If evening the DNS cache doesn’t solve your connectivity problems, try these quick troubleshooting tips-off to fix your Internet connection.
5. GETMAC
Every device that’s compliant with IEEE 802 standards has a unique MAC address( Media Access Control ). The manufacturer delegates MAC address and collects them in the device’s hardware. Some beings use MAC residences to limit which manoeuvres can connect to the network.
Sample usage and output 😛 TAGEND

You may insure more than one MAC address depending on how many network-related adapters are on your system. For precedent, Wi-Fi and Ethernet connections would have been able to separate MAC domiciles. If you would like to know more, check out what your IP and MAC address are good for.
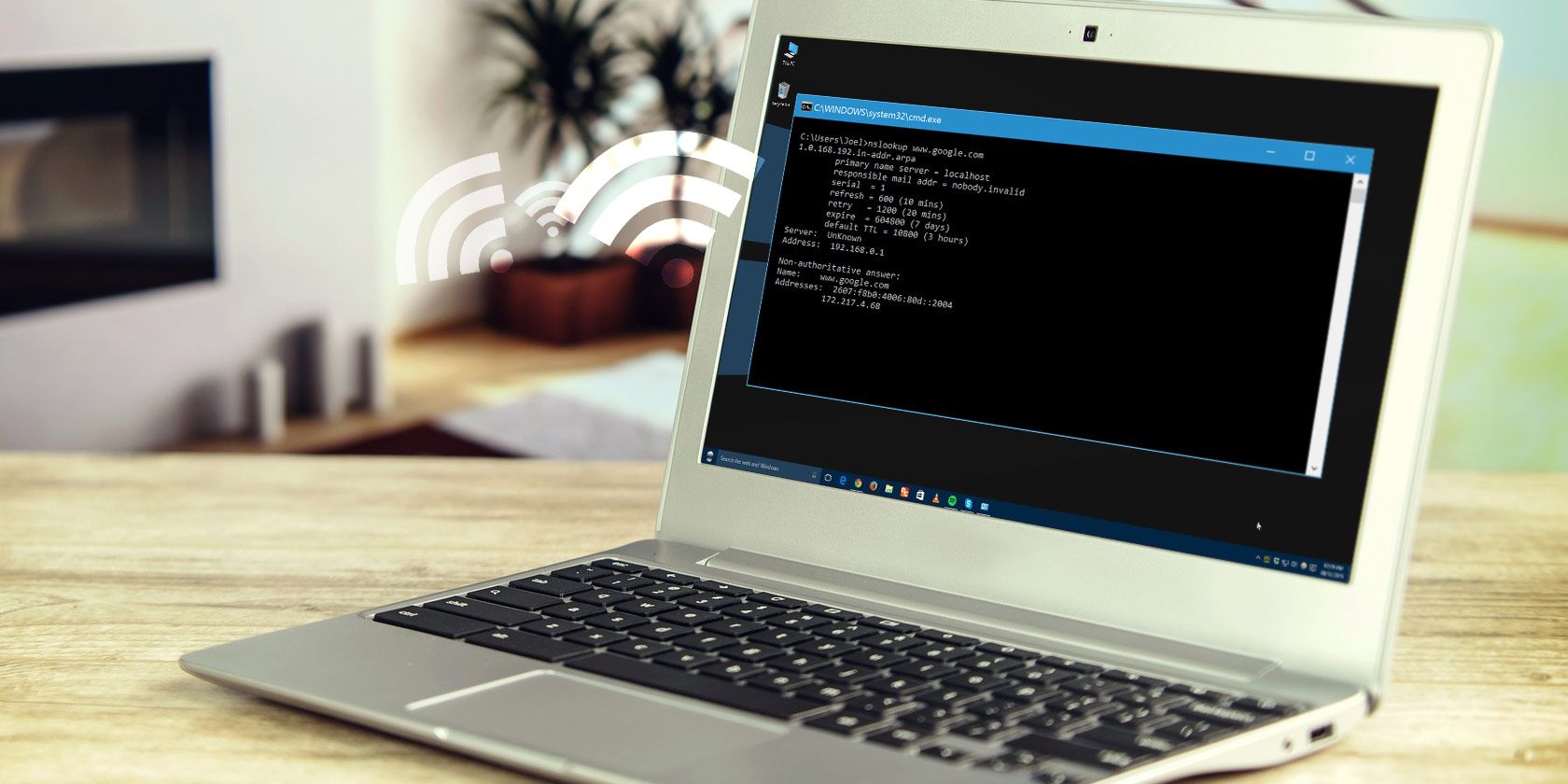
6. NSLOOKUP
nslookup stands for Name Server Lookup. It jam-pack a lot of power, but most users won’t need that capability. For regular kinfolks looks just like you and me, its main use is finding out the IP address behind a certain domain name.
Sample usage and output 😛 TAGEND

Note that sure-fire domain names aren’t tied to a dedicated IP address, which means that you may get different IP addresses every time you run the dominate. This is normal for bigger websites since they were spread their workload across many different machines.
If you want to convert an IP address into a domain name, precisely character it into your browser and experience where it extends. Not all IP addresses lead to domain names though, and countless IP addresses aren’t reachable over the web.
7. NETSTAT
netstat is a tool for network statistics, diagnostics, and analysis. It’s strong and complex but can be simple enough if you discount the advanced appearances that you don’t need to know about( presupposing you aren’t succeeding a big business or campus structure, for example ).
Sample usage and output 😛 TAGEND

By default, the bid establishes all “active connections” on your organization whether those connections are on LAN or across the internet. An active associate doesn’t mean data acting results — it could just aim a port that’s open and ready to accept a connection.
Indeed, netstat is mostly useful to regular customers for its ability to show port information, and that can come in handy when you need to forward ports.
But the word also has about a dozen switches that change what kind of information is exposed, such as the -r switch which shows a routing counter instead.
8. NETSH
netsh stands for Network Shell. It’s a cmd dictation for networking that lets you deemed and configure pretty much every system adapter on your plan in more detail and granularity than any of the preceding commands.
Running the netsh command on its own will shift the Command Prompt into system eggshell mode. There are several different “contexts” within this shell, including information for routing-related masteries, one for DHCP-related masteries, and one for diagnostics, among others. But you can use it to run individual dictations, too.
To see all network shell frameworks 😛 TAGEND

And to see all dominates within a situation 😛 TAGEND

You can instruct down one more layer to find all of the subcommands within those masteries 😛 TAGEND

So for example, you can run this command to goal all of the wireless system drivers on your organization and their assets 😛 TAGEND netsh wlan depict motorists
Network Shell’s complex enough to deserve an part essay “of ones own”. Just know that if you want to get real technological with your system configuration, you’ll probably is in need of this command-line utility.
If Network Shell left you wanting to explore more than cmd network biddings for your method, try these basic cmd authorities every consumer should know.
Network Mastery and Other Networking Solutions
For anyone brand-new to Windows networking requires, a chisel expanse comes in handy. With some invoke, you can use a variety of cmd masteries for collecting information on your system, wi-fi, and the Internet. Still, while it’s useful to always know your options, you might hanker an alternative.
Maybe using cmd dictations for your networking aren’t necessary for the specific problem you’re having. You should check out these diagnostic ploys and simple sticks for network troubles to see if there’s a answer for you in there.
Read the full essay: 8 CMD Commands to Manage Wireless Networks in Windows
Read more: makeuseof.com





Recent Comments